If you haven’t been living under a rock, you must have heard about cryptocurrency in one way or another. Examples of cryptocurrencies (crypto for short) include the very popular Bitcoin, Ethereum, and meme coins like Doge Coin, Cardano, BNB, and Tether, to mention a few.
In this article we’ll cover everything that there is to know on Ethereum, starting from the meaning of crypto currencies and how they came about.
Definition of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are virtual or digital currencies distributed by a wide range of networks and firmly secured in a decentralized system by cryptography and encryption. It is used for online transactions to purchase, transfer, and acquire both virtual and physical assets. Due to their strongly barricaded system on blockchain technology, they extremely resilient to hacks, and since they are not issued by a governing authority, they are free from tax levies or general interference from a centralized body.
How and When Were Cryptocurrency Invented?
Even though early studies about cryptocurrencies were made in the 1990s; the Era of cryptocurrencies only began in 2009, when Satoshi Nakamoto (the preferred pseudonym used by those behind bitcoin’s creation) created the first coin.
Ultimately, the introduction of bitcoin created a new wave of information on which several crypto projects were built.
This ushered the development of a new cryptocurrency, known as Ethereum, which offered a smart contract option in addition to the already existing blockchain technology for online asset security. Although Vitallik Buterin, the developer, initially submitted an article on the “Concepts Of Ethereum” in November 2013, it did not gain fame until early 2014, and by September that same year, it’s assets had sold for over $18 million.

Understanding Ethereum
Ethereum is more than just a cryptocurrency, because the Ethereum Foundation is based on a public-source-based blockchain platform that integrates decentralized applications and smart contracts into its technical mainframe.
More specifically, the Ethereum network offered three main unique and innovative features that contributed to the popularity of this blockchain technology.
1. Ether (ETH) in the Ethereum Universe: Function, Mining and More.
- The function of Ether:
The ETH is the major token or currency for the Ethereum network. They are used for completing transactions, powering decentralized applications, and finalizing payment processes. They are referred to as “gas” and are used for executing self-powered contracts known as smart contracts.
- Mining Ether
Ether is securely mined via a process known as Proof-of-work, which maintains it’s key decentralization aspect of the Ethereum network. Mining involves the use of very high computational strength to solve mathematical problems, which authenticates and validates the work done; thereafter, a reward may be issued.
Additionally, because Ethereum’s maximum number of tokens is not capped like Bitcoin (21 million coins), it is somewhat more abundant and easier to mine; however, there have been reductions in Ether, which in turn creates scarcity and increases the price.

2. Decentralized Applications (DApps or dApps):
Decentralized applications are applications that are built and run on a decentralized network connected to a smart contract and a front-end user interface. This means that no one can claim rights of ownership as they exist on the public system to avoid any failure points regarding to its security. DApps run on Ethereum tokens, or gas, which utilize smart contract in-built lines of code to perform logical functions and execute functional commands. This renders them immune to various cyberattacks and thefts.
Benefits of DApps:
- The hack-proof security offered by the blockchain technology removes risks and cryptographic tampering.
- The crystal-clear functioning reduces risks of potential manipulation and digital theft.
- The public nature of the blockchain technology fosters peer-to-peer transactions and removes potential third-party interference fees.
Downsides of DApps:
- Although the transactions 0nly require simple processes, many new users still find it difficult to navigate the platform, and this may hinder the growth of responsive users over time.
- The limited number of transactions done per second is a significant challenge to the growth of this cryptocurrency and Ethereum-based applications.
3. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are special contracts armed with the power to execute certain functions and carry out specific assignments if and when an agreement is reached between two parties.
Once an agreement has been input into the lines of code of the smart contract, they can perform functions such as digital asset transfers, multiparty system agreements, the purchase or sale of real estate, and so on.
Real-world Use Cases of Smart Contracts:
- Voting Systems
- Real Estate transactions
- Automated payment System
- Insurance
The applications of smart contracts to the real world are unimaginable; however, the terms of the agreement and specific situations should be taken into consideration when setting up such contracts.
Ethereum’s Upgrade: From 1.0 to 2.0
Ethereum 1.0
Many people are unaware of the transition from Ethereum 1.0 to Ethereum 2.0, however it market a significant turning point for the network. This upgrade was extremely sought after due to the increasing downsides associated with the Proof-of-Work algorithm (PoW) used for mining Ether.
The previous PoW required miners to solve complex cryptographic mathematical puzzles to add a new block to the network. Although this consensus algorithm is still adopted by other cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, these processes required vast amounts of computational power and excessive power consumption to do so, leading to environmental and efficiency concerns.
Additionally, the original network was becoming outdated and some concerns about its security started to rise. Therefore, all these factors contributed to the very recent “Shapella Upgrade”, an upgrade of the Ethereum’s consensus algorithm from Ethereum 1.0 to Ethereum 2.0.
Ethereum 2.0
Unlike its predecessor, the model here was different; transactions were carried out by an algorithm known as Proof-of-Stake (PoS), which utilized a different method to overcome the limitations of Ethereum 1.0.
In this model, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency (ETH) they are willing to stake as collateral for the creation of a new block to be added to the network, minimizing the energy consumption, thereby maximizing efficiency in the long run.
ETH 2.0 also adopted a genius method known as “Cryptic Sharding,” which involves the breakdown and distribution of individual transactions and smart contracts across singular networks so each one can run independently. This method proves to be more economical as it greatly increases the speed of the overall Ethereum transaction network.

Security, Efficiency and functionality upgrades
Ethereum has also undergone many solid performance and security changes over time. The three major upgrades are:
- Metropolis: Characterized by two phases, Byzantium and Constantinople, these models focused on improving privacy and anonymity between partners. The zero-knowledge proofs, or ZK-Snarks,” were introduced to allow a transaction to be concluded without knowledge of the identities of the sender and receiver.
- Constantinople: Constantinople ushered in the Ethereum shift from the Proof-of-Work to the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm. This allowed for scalability of the network and increased transaction speed.
- Istanbul: The Istanbul hard fork increases the functionality of smart contracts and improves interoperability with privacy coins. This upgrade is resilient to Distributed Denial of Service attacks, also known as DDoS attacks.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Ethereum
Decentralized finance is a financial system of transactions created for the public to eliminate intermediaries like banks and third parties, reducing the cost of transactions. The mainstay of the DeFi system is to change out native methods of deals and contracts by fostering peer-to-peer transactions to ensure an equitable distribution across all parties, individuals, and organizations in a global system. The DeFi blockchain improves asset accessibility and global interactions within its ecosystem.
Ethereum as a Hub for DeFi Projects
All DeFi projects are made possible because of the smart contract functionality associated with the Ethereum blockchain technology. Just as smart phones and devices are able to carry out specific functions at designated times, like setting an alarm at 4 p.m. with a specific ringtone or choosing a particular ringtone for a person, these smart contracts carry out designated functions involving a series of complex financial transactions when certain requirements for that functionality are met.
This process eliminates threats of theft, fraud, intermediaries, and financial autonomy as it promotes a trustless and transparent transaction. Furthermore, thanks to smart contracts and decentralized finance, it has become possible to pursue many activities such as yield farming and creating decentralized exchanges.
DeFi Applications on the Ethereum Network
1. Liquidity pool and yield farming
A liquidity pool is an incentivized scheme provided for users that participate in stabilizing the market at crucial times (such as scarcity) by providing liquidity to a pool (decentralized system tokens). By providing liquidity to these pools, they receive incentives or rewards for saving the market; think of them as unseen, paid heroes of the market.
Yield farming, or Liquidity mining, follows a similar pattern where users get interest on locked cryptocurrency. By simply holding some cryptocurrencies for a certain period of time, interest is accrued to individual accounts as a means of appreciation for contributing to the stability of the market. These interests or rewards are monitored and efficiently tracked by smart contracts.
An example is fixing your money into your local bank account for a predetermined time period with hopes of getting some additional funds (interest or rewards) at the expiration of the stipulated time
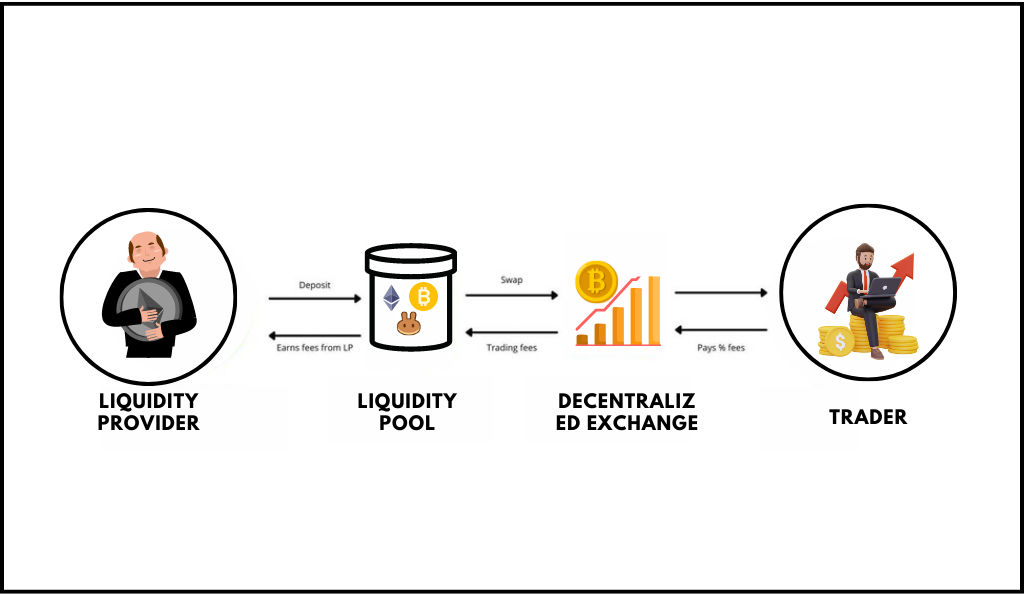
2. Decentralized exchanges
Decentralized exchanges are peer-to-peer exchanges where users retain full authority over their digital assets and maintain their power in such networks with a centralized system. By utilizing the power of blockchain technology, decentralized exchanges, or DEX, which include SushiSwap and UniSwap, have revitalized mundane routes of exchange by circumventing third-party intrusions like banks and brokerages.
Non-Fungible Tokens and Ethereum
Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, are items that represent proof of ownership of unique cyber assets. The ideology behind a NFT is simple: special items possess unique, indivisible, uninterchangeable properties that are peculiar only to that item; therefore, every NFT is different from the others. As opposed to fungible tokens such as Ether, which are divisible and interchangeable across the global network, their worth is fixed.
This singular characteristic of NFTs enables its applications in cyberspace, space, and the digital world, where assets unique in their own right that possess a worth conferred by the owner can be bought or sold. These may include pictures, videos, music collections, creative art, etc.
A mind-blowing example is the fact that the former CEO of Twitter, Jack Dorsey, sold his first tweet for $2.9 million to an Iranian investor.
Why and How NFTs are built on the Blockchain Technology
Why: NFTs utilize the hack-proof, secure technology of the blockchain to store vital and sensitive information unique to them. They contain information such as the owner’s proof of authenticity, address, and even the meta data of the owner. The blockchain acts as a fail-proof safe to house such information.
How: Smart contracts are like the blood in a human body that keeps it alive by constantly flowing. In that sense, smart contracts authenticate, confirm, and verify the information on each NFT before initiating a transaction between the parties involved.
Ethereum’s Smart Contract Competitors
While Ethereum is the first of its kind and the king of the smart contract industry, many younger blockchain systems with smart contract capabilities are vying for the throne. Among these are:
- Cardano: Cardano is unique for its verifiable smart contracts and multi-asset ledger. It also utilizes the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm of Ethereum 2.0.
- Binance Smart Chain technology: it utilizes its blockchain to directly deploy decentralized applications to its main network. Coins may be used as collateral for the consensus model.
The Future of Ethereum
Forging ahead, the possibilities of Ethereum are seemingly endless, especially with its smart contract abilities. However, the fundamental problems, which include massive power usage, an exorbitant business levy, and online traffic in Ethereum 1.0, still exist even if significantly reduced.
As we look forward to the full integration of the Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism, which is usually about 2 years from launch (September 2022), we can begin to imagine an effective turnaround time on transactions, its primal scalability, and its sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our extensive dive into the world of Ethereum has discovered many significant upsides and downsides of this innovative technology. Firstly, Ethereum is way beyond a normal cryptocurrency; it is an extraordinary, ground-breaking entity that has revolutionized the traditional way of conducting business and opened new realities to the power of blockchain.
Secondly, its smart contract functionality has fostered many peer-to-peer business transactions due to its inherent nature of transparency, authenticity, and the removal of interfering entities.
Also, Ethereum’s blockchain technology is the solid foundation on which decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are based. Users can conduct hassle-free purchases and transfers without fear of fraud, theft, or secondary interference. The public or decentralized platform provides leverage to perform complex business transactions, authenticate the identities of users, and store sensitive information all on the same network.
As modern technologies continue to emerge, it is imperative we put our ears to the ground, especially in the blockchain cyberspace. Ethereum may very well be changing our perceptions of what we thought was “impossible”.
CryptoGlobally aims to offer impartial and trustworthy data on cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and shares. Yet, we can't give financial guidance and encourage individuals to conduct their own studies and thorough checks.